A Three-Step Approach to OT Cybersecurity
Published by Leah Jones,
Digital Administrator
Hydrocarbon Engineering,
How modular in-product expansion supports organisations as OT security programs mature.

Executives and boards in industrial organisations want to understand current risk profiles and whether a recently disclosed vulnerability puts the organisation at risk. However, OT cybersecurity is less mature than IT cybersecurity. Most industrial organisations are still in the early stages of improving their OT asset inventories, relying on manual approaches for risk identification, prioritisation and remediation. OT cybersecurity maturity can also vary widely across sites within a larger organisation. Hexagon finds OT cybersecurity can be grouped into three general steps – visibility, vulnerability and comprehensive OT security and risk management. Hexagon’s PAS Cyber Integrity™ provides a modular solution that provides these capabilities and can expand as OT security needs mature.
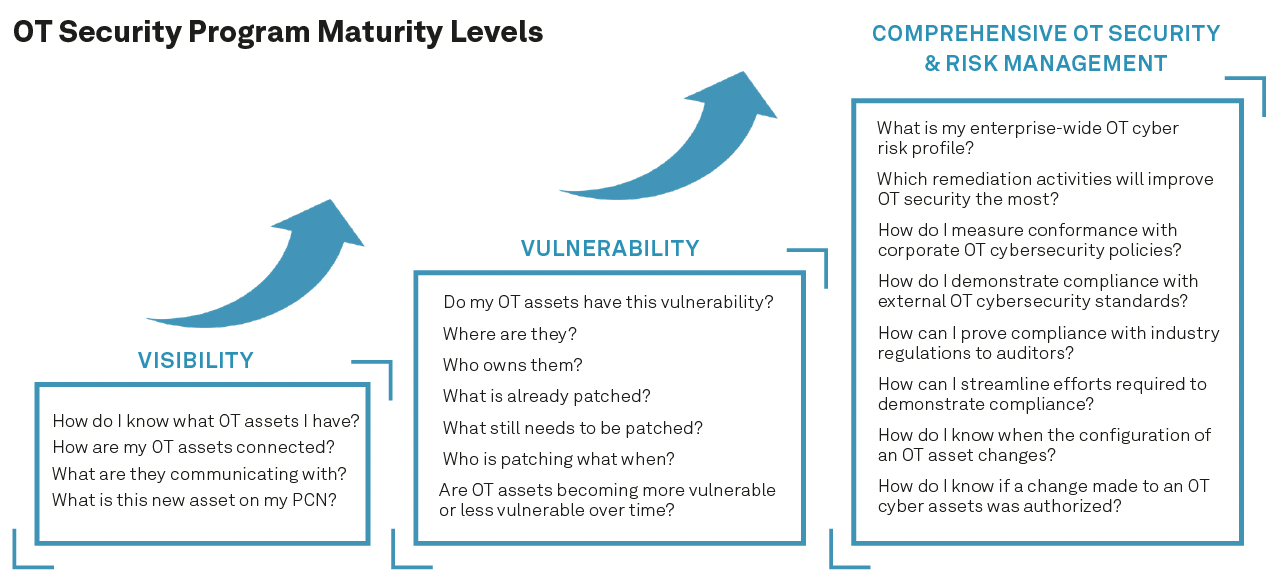
Step 1: Visibility
Obtaining an accurate and detailed OT asset inventory is foundational for improving OT cybersecurity maturity. It is also a prerequisite for OT cyber vulnerability and risk management, meeting internal and external compliance requirements, understanding potential attack vectors and investigating incidents.
Cyber Integrity – Inventory provides unmatched industrial control systems discovery and topology mapping — down to Level 0 devices — without passive network detection limitations and active network polling risks.
- Automatically discover IT and OT assets (Level 3 – Level 0) for over 120cross-vendor OT systems.
- Maintain a complete inventory of IT and OT system hardware and software, I/O cards, firmware, applications, and any custom data.
- Identify compromised endpoints, their relationships and connections with other endpoints and their role in the process.

Step 2: Vulnerability
With a comprehensive OT asset inventory in place, vulnerability management is the next step. Identifying and remediating known vulnerabilities is one of the best ways to reduce critical infrastructure risks. However, despite many known vulnerabilities for industrial control systems, OT teams often struggle to identify vulnerabilities.
Cyber Integrity – Vulnerability Management includes inventory management and identifies and assesses vulnerabilities hidden in industrial infrastructure.
- Automatically compare and assess the latest vulnerability information from the United States National Vulnerability Database (NVD) – and further enriched by PAS cybersecurity analysts – with inventory data to identify OT assets with vulnerabilities that may put production systems at risk.
- Obtain a centralise, unified view of current patch levels across all managed cyber assets.

Step 3: Comprehensive OT Security & Risk Management
With a detailed and accurate OT asset inventory and operational vulnerability and patch management in place, the final stage of maturity is to enable capabilities for comprehensive OT security baselines, configuration management, policy management and workflows to manage compliance.
Cyber Integrity – Enterprise includes inventory, vulnerability and patch management, and adds in-depth Level 3 to Level 0 OT asset configuration management, comprehensive cybersecurity configuration baselining, unauthorised configuration change detection, workflow-driven vulnerability remediation and incident response, risk analyses, compliance workflows and reporting and backup and recovery support.
- Track configuration changes against established baselines.
- Establish configuration policies to monitor for unauthorised changes to control strategies, device inventory, asset configuration, and logical and graphical files.
- Enable workflows and documentation for vulnerability remediation and compliance with NIST, ISA/IEC 62443, NERC CIP, ISO 27001/2, the NIS Directive, and other regulations.
- Capture full configuration backups to support in-depth forensic analysis and speed recovery in the event of a worst-case scenario.

Built for Today and Tomorrow
The cyber risk for critical infrastructure and process industries is greater than ever. Digitalisation projects and remote work have expanded the attack surface. The modular licensing and deployment capabilities of Cyber Integrity provide flexibility to address current needs and expand to support future needs as sites advance their OT cybersecurity maturity.

About Hexagon
Hexagon is a global leader in digital reality solutions, combining sensor, software and autonomous technologies. Hexagon puts data to work to boost efficiency, productivity, quality and safety across industrial, manufacturing, infrastructure, public sector, and mobility applications.
The company's technologies are shaping production and people-related ecosystems to become increasingly connected and autonomous – ensuring a scalable, sustainable future. Hexagon’s PPM division empowers its clients to transform unstructured information into a smart digital asset to visualise, build, and manage structures and facilities of all complexities, ensuring safe and efficient operation throughout the entire lifecycle.
Hexagon (Nasdaq Stockholm: HEXA B) has approximately 21 000 employees in 50 countries and net sales of approximately €3.8 billion. Learn more at hexagon.com and follow Hexagon @HexagonAB.
Read the article online at: https://www.hydrocarbonengineering.com/special-reports/21062022/a-three-step-approach-to-ot-cybersecurity/
You might also like
The Hydrocarbon Engineering Podcast - Travelling towards sustainability: exploring the economics of e-fuels
In this special episode, a panel of experts from Johnson Matthey, A.P. Moller - Maersk, Honeywell, HIF Global and the Methanol Institute provide a clear analysis of the factors influencing e-fuel pricing, the economic challenges, and strategies for cost reduction.
Tune in to the Hydrocarbon Engineering Podcast on your favourite podcast app today.

