The modern hydrocarbon industry – spanning wellheads, burners, LNG terminals, and more – is facing unprecedented pressures to reduce environmental impact, circularise supply chains, and digitalise operations. These challenges demand a fundamental operational shift toward greater efficiency, but achieving success requires the right tools.
Oil and gas companies are quickly recognising the need for a foundation of digital solutions to build on their investments and make an impact. The artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities included with today’s analytics platforms are increasingly providing the transformative power required to meet these needs, representing a critical strategic imperative throughout downstream and LNG operations. These tools enable decisive algorithmic advantages in these sectors.
Paired with the expertise of their subject matter experts (SMEs), oil and gas companies are leveraging advanced analytics applications to gain new visibility into their process data, helping optimise their operations with little capital investment required. With AI-equipped advanced analytics platforms deeply embedded in the operational realities of this industry, organisations are witnessing a profound integration of intelligent analytics into core processes, moving beyond isolated projects to a point where data-driven insights actively drive optimal outcomes across all operations.
Ensuring reliable flow and pipeline integrity
Transportation and storage operations are increasingly leveraging AI and ML algorithms to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable operations. This is achieved by integrating data from sensors – such as pressure, temperature, and flow – cathodic protection systems, and inspection logs in a centralised monitoring platform.
ML models, such as random forests and support vector machines, can be employed to predict the likelihood of leaks with up to 80% accuracy. By analysing pressure transients and correlating them with historical leak events and environmental factors to generate risk scores, plant personnel can efficiently prioritise maintenance and proactively inspect high-risk segments to potentially prevent multi-million-dollar incidents.
Furthermore, operational data analysis in advanced analytics platforms and the application of ML techniques are being used to improve compression and pumping optimisation. The insights generated by these tools help identify critical operating points where processes can be optimised or energy consumption can be reduced.
Additionally, this software is being used to optimise crude oil and natural gas inventory levels, market prices, and logistical constraints. Time series forecasting models, such as ARIMA and Prophet, are employed to predict future storage needs with up to 95% accuracy, optimising filling and withdrawal schedules to minimise vessel demurrage. The associated cost savings range from US$25,000 – US$100,000 per day, with maximised throughput adjusted for anticipated market fluctuations.
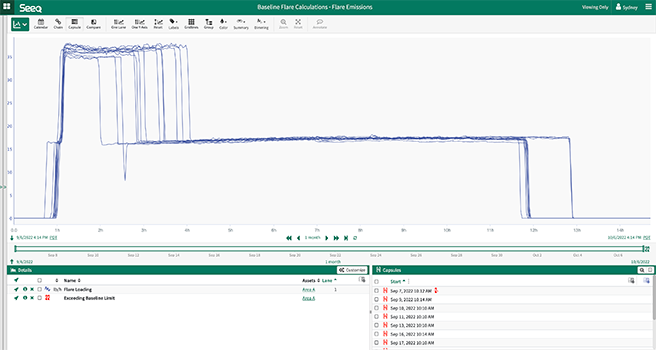
Figure 1. Using Capsule View in Seeq, a team of data analysts and process experts at a Canadian refinery identified periods of interest to establish a baseline operating definition, off which models for issue identification were constructed.
Refining for maximum value
Integration of AI/ML via advanced analytics platforms is also enhancing profitability and throughput in downstream refining operations across numerous complex and energy-intensive processes.
For example, these tools are providing ML-enhanced advanced process control (APC) systems with the ability to adapt to changing feedstocks and operating conditions, increasing high-value product yields by 1 – 3% in various facilities, while reducing energy consumption by 2 – 5%. These effects are achieved by identifying optimal reactor conditions that maximise desired output and minimise by-product formation.
Additionally, vibrational data analysis aids predictive maintenance and asset reliability models in critical refining units. By also employing spectral analysis and correlation with historical failure modes, advanced analytics platforms can often provide a lead time of several weeks before failure of equipment like centrifugal pumps, where unplanned downtime can cost upwards of US$500,000 per day in lost production.
Energy analysis and management is also critical in the downstream sector, accounting for 30–40% of operating costs. By monitoring usage patterns across different units and applying statistical process control (SPC) in real time, software systems can detect and alert plant personnel to anomalies, identify energy waste, and optimise utility usage, such as steam and electricity. These insights routinely prove to reduce utility consumption costs by 5 – 10%.
Optimising liquefaction and shipping
The LNG value chain, encompassing liquefaction plants and shipping terminals, also stands to benefit significantly from AI/ML-driven optimisation.
Liquefaction plant optimisation leverages compressor, heat exchanger, and cryogenic systems analysis, along with ML models – such as Gaussian Process Regression – to predict optimal operating conditions and maximise LNG production rates. Average datapoints show increased outputs of 0.5 – 1.5% with 1 – 3% energy consumption reductions after applying these models.
Shipping and logistics represent additional areas for optimisation with centrally connected advanced analytics platforms. These tools are frequently used to integrate vessel scheduling, weather pattern, and terminal operation data. Equipped with this information, AI-powered route optimisation algorithms regularly reduce transit times by 5–10%, subsequently decreasing fuel consumption, which accounts for 40–60% of voyage costs. These enhancements also improve overall supply chain efficiency and reliability.
In terminal operations, advanced analytics platforms can optimise import and export functions by analysing berthing schedules, loading/unloading rates, and storage level data. As predictive models improve, they are consistently forecasting terminal congestion with up to 80% accuracy, facilitating schedule adjustments to improve efficiency and minimise demurrage costs.
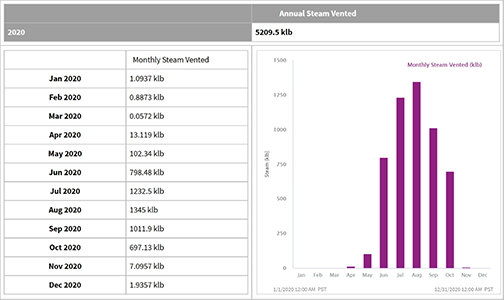
Figure 2. By analysing historical data, the subject matter experts (SMEs) at a major refiner quantified the probability of a boiler trip, which causes significant upsets in a single boiler operation. They then weighed the risk of a trip against the steam and energy savings of running a single boiler to determine the best mode of operation.
Operationalise intelligence across the value chain
The strength of advanced analytics platforms lies in the abilities to connect, contextualise, analyse, and visualise operational data across downstream and LNG operations, empowering engineers, operators, and business leaders with the tools required to:
- Unify disparate data sources: by seamlessly connecting to diverse arrays of data historians, control systems, maintenance management systems, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, plant personnel gain a complete operational view, which provides the foundation for optimisation.
- Contextualise data for meaningful insights: raw data alone is insufficient for analysis, but built-in capabilities to cleanse, contextualise, and frame data provide the necessary domain-specific understanding that makes AI/ML analysis impactful and relevant to specific operational challenges across the value chain.
- Empower the SME: recognising that AI/ML’s true power lies in augmenting human expertise, leading analytics platforms are equipped with intuitive interfaces that prioritise enhancing SME knowledge. These individuals’ input and accumulated learnings form the bedrock of effective AI/ML outcomes because process experts must guide model selection and tuning, validate outputs, and translate algorithmic insights into tangible operational improvements driven by practical understanding.
- Facilitate collaborative AI/ML deployment: leading advanced analytics platforms provide an environment where data scientists and domain experts can collaborate to build, deploy, and scale AI/ML models within their specific operational contexts, leveraging the latest tools and libraries.
- Drive actionable intelligence and operationalise models: true value is realised when insights are translated into tangible improvements, made possible when visualisation and collaboration tools deliver AI/ML outputs for easy understanding and clear recommended action. Only in these cases can AI drive real-world efficiency, safety, and profitability improvements.
Embrace algorithmic excellence
The future success of the hydrocarbon industry is inextricably linked to the strategic embrace of digital transformation, with AI/ML augmentation. From maximising refinery yields and streamlining LNG logistics, the algorithmic advantage is not a distant aspiration, but a present-day reality.
Companies strategically leveraging the power of AI and ML across downstream and LNG operations are well-positioned to not only navigate current pressures, but to thrive in the evolving energy landscape. Advanced analytics platforms provide the foundation to achieve algorithmic excellence with intuitive tools that empower SMEs to drive tangible value and shape an efficient, safe, and sustainable future for the entire industry.
Written by Shaista Mallik, Seeq Corp.